COUNTRY PAPER OUTLINE
The following outline was provided to all participants before the Madras Workshop to facilitate the preparation of country papers.
This outline covers information on existing and estimated potential production capacity, sources of repair and maintenance services, mechanisms and channels used for distribution, human resources development, as well as technical cooperation among developing countries. In the preparation of the paper, you may need to consult with colleagues from other Departments, e.g., those from Science and Technology and Industry and non-governmental organizations (NGOs). The information provided will be used in the substantive servicing of the above-mentioned Workshop to be convened by ESCAP at Madras, India, from 5 to 14 September 1995. The country papers received will also be reviewed for possible inclusion in a publication to be issued by the ESCAP secretariat following the Workshop. You are kindly requested to attach or bring with you to the Workshop graphic illustrations of assistive devices produced in your country, including technical drawings and photographs of publishable quality.
Definition of term "assistive devices"
The term "assistive devices" refers to all devices that increase the capacity of people with disabilities to function in all aspects of daily living, including work and leisure. The following are some examples of assistive devices (the list is not comprehensive):
- Devices for people with mobility impairments: e.g., wheel chairs, trolleys, tricycles, calipers or braces, crutches, walkers and artificial limbs.
- Devices for people with sight impairments: e.g., braillers, low-vision devices, white canes, adapted precision measurement instruments, educational devices and adapted toys.
- Devices for people with hearing impairments: e.g., hearing aids and telecommunications devices for deaf people (TDD).
- Devices for people with cerebral palsy: e.g., adapted crockery and cutlery.
A. Need for assistive devices
- What statistics and information are available on the overall need for the different types of assistive devices in your country? Please indicate the source(s) of statistics and information.
- To what extent is the need met at present?
- How is that need met?
- How much (estimate percentage) of the overall national need for different types of assistive devices is met through import? Please include:
- i) Main sources of import;
- ii) Main types of devices imported;
- iii) Percentage of total imported devices that are purchased and percentage that are donated;
- iv) Remarks on customs duties and customs clearance procedures concerning the import of assistive devices (please obtain information from those engaged in the import of assistive devices).
B. Policy
- Is there an explicit government (central and/or provincial) policy concerning the indigenous production, import and distribution of assistive devices?
- What are the main features of the government policy(ies)?
- What mechanisms exist for the implementation of those policies?
- Do national standards exist for assistive devices used within the country?
- What are the issues concerning standardization of assistive devices in your country?
- To what extent is your national standards body involved in standardization matters concerning assistive devices? (Give the full title and address of the division in your national standards body which is concerned with assistive devices.)
C. Production capacity
Please specify for relevant categories (e.g., wheel chairs, calipers, prosthetic devices):
- Number of units produced per month;
- Actual production in country
- (i) By province or state;
- (ii) By workshop or production unit;
- Estimated potential production capacity in country (list for main categories of assistive devices produced);
- Reasons for limits to production capacity (specify financial, technical or other).
D. Repair and maintenance services
Are repair and maintenance services for assistive devices provided by:
- Workshops for production of assistive devices?
- Vehicle/bicycle repair workshops?
- Carpentry workshops?
- Welding workshops?
- Others? (please provide additional information)
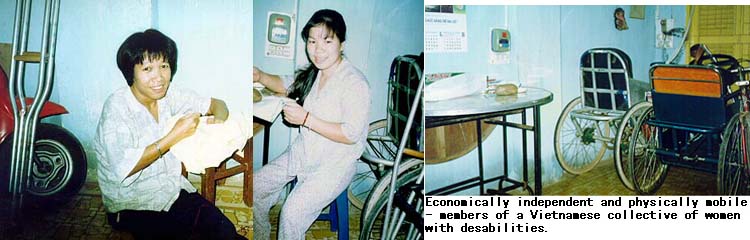
E. Distribution
- What are the mechanisms for distributing assistive devices to people with disabilities in your country?
- What is the procedure for a person with a disability to follow in order to obtain an assistive device?
F. Technology
- Please provide information on the type of technology and materials used for the production of each category of assistive devices in your country.
- Regarding techniques used in production:
- (i) Are electrical free-standing machines used in production?
- (ii) Are electric hand tools used in production?
- (iii) Specify the types of equipment used.
- (iv) Specify types of components made within the country.
- (v) Specify the types of raw materials which are indigenous to your country.
- (vi) Specify types of components imported and their sources.
- Unit cost of each type of device produced. (Please indicate equivalent of local currency to US dollars, if stipulating unit cost in local currency)

G. Personnel
- Please define the categories of assistive device technicians in your country (assistive device technicians may include, for example, prosthetists/orthotists, orthopaedic shoemakers, brace makers, mobility aid technicians, machinists, welders and fitters).
- Please give information on the duration and subject areas of the training curricula of each category of technicians identified in the previous questoin.
- What training is available within your country for the technicians identified?
- Please give key points on these types of training schemes in your country:
- (i) Apprenticeship schemes;
- (ii) Vocational colleges;
- (iii) Graduate institutions.
- Type of employment of technicians in your country: (estimate each as a percentage of the total number of technicians employed)
- (i) Self-employed;
- (ii) Employed by private companies;
- (iii) Employed by non-profit organizations;
- (iv) Employed by the Government.
H. Institutional support
- Please identify sources of institutional support for the indigenous production and distribution of assistive devices in your country: (give names)
- (i) Government ministries or departments;
- (ii) Private companies;
- (iii) NGOs (local and international).

I. Technical cooperation
Technical cooperation among developing countries (TCDC) involves the contribution of technical assistance and in-country expenses for personnel from other developing countries, usually on a reciprocal basis.
- Is your Government interested in participating in TCDC exchanges to promote the production and distribution of assistive devices in the ESCAP region? If yes:
- (i) As a contributor of host country technical assistance (including training) programme? (yes/no)
- (ii) Please specify areas of technical assistance which your country would be willing to contribute in a host country TCDC programme, and departments/ministries/ NGOs in your country willing to contribute the technical assistance and local expenses.
- (iii) As a beneficiary of technical assistance (including training) programmes in other developing countries in the ESCAP region? (yes/no)
- (iv) Please specify areas of need to be met through participation in a TCDC programme.
Go back to the Contents
ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMISSION FOR ASIA AND THE PACIFIC
Production and distribution of assistive devices for people with disabilities: Part 2
- ANNEX (Country paper outline) -
ST/ESCAP/1774
UNITED NATIONS PUBLICATION
Sales No. E.98.II.F.7
Copyright c United Nations 1997
ISBN: 92-1-119775-9
