Part Two: The Key Elements of Evaluation of CBR
The contents of evaluation in CBR consist of three parts: (1) Evaluation of management in CBR, (2) Evaluation of implementation in CBR, and (3) Evaluation of social impacts of CBR.
1. Evaluation of management in CBR
The realization of the CBR goals depends on a management mechanism, which should be scientific, reasonable, effective and sustained. The main duties of management are planing, organizing, allocating personnel, guiding, controlling and blazing new trails, etc. The management of CBR includes policy-making, planing, training of personnel, implementation at all levels, provision or resource, monitoring and evaluation. It involves government and it's departments, NGOs, communities and disabled person's families.
(a) Government's commitment: Government plays a leading role in CBR programme. Government should be involved in making policy and regulations relating to CBR, fitting CBR plan into the social development strategy, taking action, comprehensive study, overall planning, coordinating among sectors and systematic implementation.
- The list below shows what are the evaluation contents for government in CBR programme :
- (i) Integrate CBR programme with the government's working goals and local social development strategy.
- (ii) Set up CBR leading group, headed by a community leader consisting of departments concerned, and set up a special office with full time persons to cope with the daily work.
- (iii) Make CBR plan.
- (iv) Use the feasible network of community, for instance, the primary health care network, social security system.
- (v) Play an important role in the overall coordination among the sectors involved in CBR programme.
- (vi) Make and implement roles, regulations and the staff duties.
- (vii) Establish and perfect CBR resource center.
- (viii) Allocate personnel and set up professional consult group.
- (ix) Financial support (amount, allocate and expenditure)
- (x) Evaluation should be carried out regularly.
(b) Sectors concerned should take the respective responsibilities and work closely
Due to the special circumstance of disabled persons, the diversity of their needs, the broad extents of their participation in social life and the challenges of achieving their rehabilitation goal, it is essential to make sectors concerned take on their own responsibilities in CBR services and work collaboratively to offer timely referral services. Each country and region has it's own characteristics in policy, administrative mechanism, social structure, etc. The government should identify the main sectors needed for the development of CBR and clarify their responsibilities.
-
(i) Public health Sector
- Establish and perfect primary health care network.
- Training CBR professionals .
- Set up or provide training place and facilities.
- Guide and offer referral services in medical rehabilitation for people with disabilities.
- Improve public health, reduce disease, prevent disabilities.
-
(ii) Education Sector
- Make laws and regulations in order to protect disabled people's right in education.
- Conduct integration education .
- Create education conditions which is based on families and community.
- Launch education project for people with visual impairment and carry out anti-illiteracy education for disabled persons.
-
(iii) Labour (or employment) sector
- Make laws and regulations to protect disabled people's right of work.
- Set up welfare enterprises or shelter workshops to arrange job for disabled persons.
- Through multiple channels at various levels and in a variety of forms to assist disabled persons to obtain job.
- Create opportunities and condition to provide technical training for disabled so as to upgrade their skills and techniques.
- Conduct vocational training projects for job placement.
-
(iv) Social Affairs (or civil affairs) Sector
- Make laws, regulations, and preferential policy to secure and improve the life of disabled persons.
- Provide relief and subsidies through various channels for disabled persons living in poverty .
- Provide social welfare services and placement.
(v) Other Sectors
- CBR services bring together a wide range of partners, for example, culture, sport, women, child, justice, defence, etc. Sectors assume their responsibilities for policy making, planning and carry out CBR programme.
(c) Non-Governmental support
NGOs can participate in CBR services in many aspects. There are many types of NGOs, for instance: organizations representing various disabilities, religious group, charity organizations, professional societies, funding organization, etc.
- The evaluation of NGO's support in CBR should put emphasis on the following contents:
- social mobilization and awareness creating.
- take part in making CBR plan.
- training manpower for CBR programme.
- cooperation with other sectors or organizations concerned to implement CBR programme.
- provide technical support and referral services.
- organize volunteers to participate in CBR activities.
- launch CBR project for demonstration.
- conduct research project on CBR.
- provide welfare activities and fund assistance.
(d) Communities involvement
- The developmental motive and force come from the community itself. Community's involvement include the follow main aspects:
- integrate CBR programme with the community developmental plan.
- provide fund support.
- know well the rehabilitation needs of disabled people.
- fully utilize community's resources(manpower, network, facilities, institution, material, etc.).
- encourage and mobilize community member, disabled people and their family members to participate in CBR programme.
- educate community, create a sound environment and atmosphere for disabled people.
- extent appropriate rehabilitation skill.
2. Evaluation of implementation in CBR
(a) Evaluation of CBR delivery system
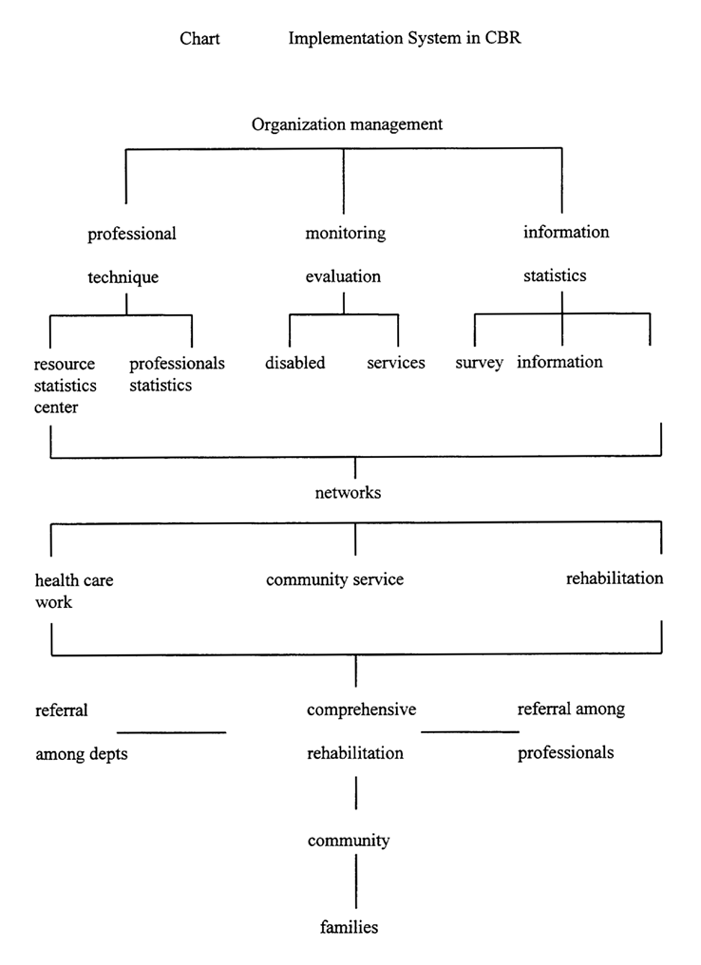
Most countries in Asia and the Pacific region depend on the public health care network, social security network, women organizations, child health care and person's organizations. These networks form the backbone of CBR delivery systems and referral systems, with which disabled persons can get rehabilitation service at family, community through national levels. An effective CBR network should be provided with four functions, namely, organization management, professional technique, monitoring and evaluation, information and statistics.
-
(i) Organization management system: This system consists of sectors concerned and administrators. To provide good CBR services for disabled people, sectors concerned should maintain a close cooperation in the work to bring about the overall effect of services.
-
(ii) Professional technique system: This system consists of resource center and rehabilitation professionals.
-
Resource center: WHO recommended many departments or units which can play roles in management, coordination, implementation, professional guide, personnel training, monitoring and evaluation of CBR. The resource center should be established in co-operation with the existing centers or institutions, for example, health care facilities, rehabilitation centers, educational facilities, vocational facilities, legal structures, welfare facilities, etc. The evaluation to a resource center should base it's responsibilities in CBR services.
-
Rehabilitation Professionals: As rehabilitation services are facing various categories of disabilities, multiple professional fields are needed for the rehabilitation consumers. For instance, people with physical disabilities need orthopaedic doctors, neurological doctors, PT, OT, equipment or aids. If the service receivers are adult, they need vocational training of various kinds and also barrier-free facilities; people with mental retardation need early identification, psychological consultant, education, vocational training, etc. Professionals, teachers, family members and disabled people may work together as a team. Rehabilitation professionals are working in various fields at different levels, including community-based level, intermediate level, provincial and national level. In fact, this professional system is the rehabilitation referral system. The evaluation of the professionals should be conducted in accordance with their role and duty in rehabilitation services.
-
(iii) Monitoring and evaluation system
The evaluation of this system includes monitoring and evaluation of rehabilitation effect on the disabled individual and the services provided. Monitoring and evaluation in CBR have been emphasised by WHO, UNDP, UNICEF, and other organizations and institutions. Monitoring and evaluation may be done by staff members within the community or by people from the outside for the purpose of improving the CBR service. -
(iv) Information and statistics system
Depending on the various kinds of forms of information and statistics to indicate work progress, quality and quantity, resource input and output, etc. The written forms should be sent to the related departments and persons in time to keep them informed on the implementation of CBR programme. This system also includes the dynamic survey on disabilities, exchange of information and data, work experience as well as the rehabilitation effect on disabled individual, etc. See Chart Implementation system in CBR.
-
(v) Evaluation the goals of comprehensive rehabilitation service achieved in CBR programme
The concept of rehabilitation lays stress on: functional training of disabled individual; interventions in changing or adapting the environment; equalization of opportunities of disabled persons in the general system of society; and protection of human right of disabled people. Community-based rehabilitation means the services through which all disabled people can get access to rehabilitation including health care, educational, vocational and social aspects, etc., so as to reaching the rehabilitation goals. The four aspects below should be taken into account in the evaluation of comprehensive rehabilitation services in CBR programme:
- Services in medical rehabilitation: It includes screen and diagnosis disabilities, functional assessment, identify the rehabilitation needs of disabled, making rehabilitation plan for disabled individual, functional training disabled and disability prevention, etc. The list below for an example shows the evaluation contents in medical rehabilitation services:
- (a) the rate of disabled surveyed;
- (b) the rate of making rehabilitation file and record for disabled;
- (c) the rate of making rehabilitation plan for disabled;
- (d) the coverage rate of medical rehabilitation services for disabled;
- (e) the improvement rate of functional training of disabled;
- (f) the changes of disability prevalence.
- •
- •
- •
- Services in educational rehabilitation: It includes regular education and special education for disabled people, while providing ideological and cultural education, strengthen physical and psychological compensation and vocational and technical training. Creating access to independent living for disabled. The examples below show the evaluation contents in educational rehabilitation services:
- (a) the rate of health and rehabilitation education to the community masses;
- (b) the enrolment rate of disabled children;
- (c) the training rate of parents or guardians of disabled children;
- (d) the anti-illiteracy rate of disabled people;
- (e) training rate of Braille for people with visual impairment.
- •
- •
- •
- Services in vocational rehabilitation: "Getting work" is one of the basic human rights. Vocational rehabilitation is an important task in the overall rehabilitation process as well as a measure for independent living of disabled persons. The examples below show the evaluation contents in vocational rehabilitation service:
- (a) vocational training rate of disabled persons;
- (b) The employment rate of disabled persons;
- (c) the increasing rate of income of disabled persons;
- •
- •
- •
- Services in social rehabilitation: Social rehabilitation means the measures through which disabled persons can take an active role in society and live a independent life with full participation in family life and social activities and enable disabled people realize self-esteem and self-actualization. In conformity with the ultimate rehabilitation goals, CBR programme should provide social rehabilitation services. The examples below show the main points in the evaluation:
- (a) the changes of participation in social life of disabled persons.
- (b) the change of barrier-free facilities for the accessibility of disabled persons to roads, buildings and houses.
- (c) the change of facilities and accommodations for disabled persons at places of cultural, sports, recreation, etc.
- (d) the chance of activities for disabled persons.
- •
- •
- •
3. Evaluation of social impacts from CBR
CBR is a course with one of the main purposes of making socially beneficial results. It appeals to create a social atmosphere with equality, justice, solidarity integration and dignity, An ideal CBR programme should be founded on positive attitude changes.
Usually the evaluation of social benefits is conducted by means of observation, discussion, questionnaire and interview, etc. Some examples are given below.
(1) the opinion of the community leaders on the CBR programme.
(2) the opinion of the community mass on the CBR programme.
(3) the opinion of the disabled persons on the CBR programme.(or the approval rate of disabled persons to the CBR programme).
•
•
•
Evaluating Community Based Rehabilitation :
Guidelines for Accountable Practice
By Dr. Tizun Zhao, Joseph K.F. Kwok Ph.D, J.P.
