Vocational Rehabilitation for Recovered Mental Patients in Hong Kong
Deborah Wan
Chief Executive Officer, New Life Psychiatric Rehabilitation Association Hong Kong
Abstract To help mental patients integrate into the community is not an easy task. However, to re-instill the work element to their daily life forms the significant factor contributing to the successful integration. This article aims to briefly introduce the current practice of vocational rehabilitation for recovered mental patients in Hong Kong. Besides, different forms of work and activities and the varied modes of vocational services for recovered mental patients are also describled and illustrated.
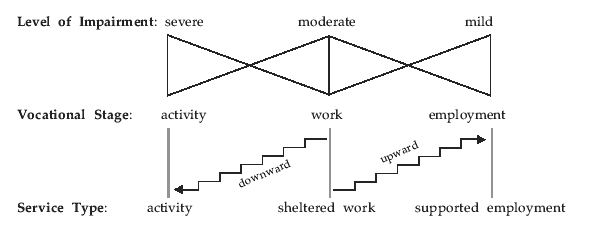
The objective of vocational rehabilitation is to enable disabled persons to participate in productive and gainful employment. In my point of view, vocational rehabilitation covers three important stages of a disabled person's daily life: activity, work and employment. Some recovered mental patients may go through all these stages whereas some may remain in one stage for a long time. It all depends on the level of ability and capability of an individual person. The diagram below illustrates the situation describled.
 D
DIn the vocational rehabilitation of recovered mental patients, the primary aim is to induce a sense of value that can help a person feel valuable and is able to carry out meaningful daily activities. This is especially true for those who have been recently discharged from mental hospitals. Examples are the work activity programmes of activity centres, work programmes of the long stay care homes where clients are assisted to engage in meaningful daily activities and to regain a feeling of value in their lives. Under such circumstances, they may not be able to get any monetary reward but they can earn the respect and value of being a person. Very often, rehabilitation workers are not fully aware of the importance of a meaningful activity for recovered mental patients which is in fact an important element proceeding to engagement of work.
Work, in this context, means sheltered work which refers to a protected working environment for workers to receive training, incentive payment for attendance and wages for work completed. Sheltered workers are assisted to develop work habits, co-work with others, and work under pressure and stress. Some sheltered workers (approximately 20 percent) could move upward to supported and open employment and the remaining 80 percent are appropriate to remain in sheltered workshops due to chronicity of their illness and the low level of productivity. Sheltered workshops in Hong Kong have been evolved from engaging in simple assembly and packaging work to a more sophisticated production line in printing, woodwork, sewing and laundry. Such inevitable change is due to the move of Hong Kong's industry to Mainland. To cope with such change, a new trend of producing own products is developed. Self produced products include hand-knitted shawls, fabric bags, woodcrafts, costume jewellery, etc. Another new development is to move from indoor work to outdoor to undertake work training and job orders such as car washing, office cleansing, estate maintenance, swimming pool cleansing, park cleansing, etc. Such new training and work mode can facilitate the trainees to move a step further to seek employment opportunities in cleansing service and it has been witnessed in the past years that sheltered workers can move upward towards the goal of open employment.
Here in sheltered workshops, workers learn to adjust to simulated working conditions and to gain wages in accordance with the work done. Workers are encouraged to work diligently so that they can earn more. In addition, workers have to be psychologically prepared to earn their own living instead of being dependent on social security benefit. This is the trend that rehabilitation workers should put more emphasis on.
Employment means to attain a job in which a person's ability and capability are utilised to fulfil the job requirements in return for remuneration of the work done. A person's value is affirmed through job satisfaction and attainment. Employment, in this context, refers to both open and supported employment. Open employment means an employment in the open competitive market. Supported employment refers to provision of on-going support to people with disabilities in employment which is an integral part of vocational rehabilitation. It allows people with disabilities to work in an integrated open setting with necessary support services and to have access to the usual benefit of having a job such as income at market rates and job security. It is a welfare-oriented service without an employer/employee relationship between the service providers and the service users. The supported employment team is staffed by social workers, marketing personnel and job coaches. Supported employment services for the recovered mental patients are practised in the modes of individual placement, mobile crew and simulated business. Individual placement is to provide on-going support to both employee and employer for a period of time so that the placed worker can adapt and adjust to the new work environment, usually intensive follow-up and continuous support will be given to the prospective employee. A mobile crew is a team of workers who perform contract work such as car washing, cleaning of parks or premises, lawning, etc. Usually a job coach is assigned to work with a team of workers and the job coach will withdraw support when the mobile crew is able to operate independently. Simulated business is a business like setting in which disabled persons are trained as salespersons, storekeepers and store managers. Examples are convenience store, market stall, stationery shop, cafeteria, etc. Very often a job coach is provided in each simulated business to train the clients and to conduct the business. The job coach will fade out when the business has been established and operated smoothly.
Clients, in supported employment services, are assessed for their motivation and suitability and then will be placed for work after trial. Clients are assisted in different stages to test their suitability as well as supported by job coach during the placement until they are successfully discharged.
For successful cases of recovered mental patients, we have witnessed their significant changes from very passive and withdrawn persons to active, outspoken and confident persons. Some of them even appeared on mass media to share their joy and expectations. Moreover, in terms of personal value and contribution, they are able to stand on their own feet and earn a decent living without receiving any social security payments.
The primary goal of rehabilitation for recovered mental patients is to assist them to integrate into the community and they being the "users" are the focal point of the service. I have initiated and motivated the residential staff in social rehabilitation service to walk out of their parameters of residential homes and to accompany clients in their work place as job coaches. Instead of asking residents to seek for work and employment, the staff have a duty to assist them in vocational rehabilitation. We have made a bold attempt locally and have achieved astounding result. One example is the halfway house staff works as job coach to assist clients to undertake a cleansing contract in the nearby area. They themselves monitor their clients' progress or suitability in the job or employment. Upon return to halfway houses, they can prepare them progressively for discharge from halfway houses if clients are successfully employed. To induce this new concept and direction, we have to change the staff's attitudes and perception that they are ready and willing to accept the changing mode of service. I am sure that we are on the right track since the rehabilitation goal is composed of social and vocational aspects. Undoubtedly, to really achieve the true integration of recovered mental patients into the community, the dedication and commitment of personnel in the field of rehabilitation is of utmost significance.
Printed by : EMV Jockey Club Desktop Publishing Centre
Association for Engineering and Medical Volunteer Services
