Bus stop
| Application | General | Urban application | Information technology | Rural application | Safety | |||
| External environment | Public building | Housing | Public transport | |||||
| Physical | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
| Visual | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
| Hearing | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
| Intellectual | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
Recommendation:
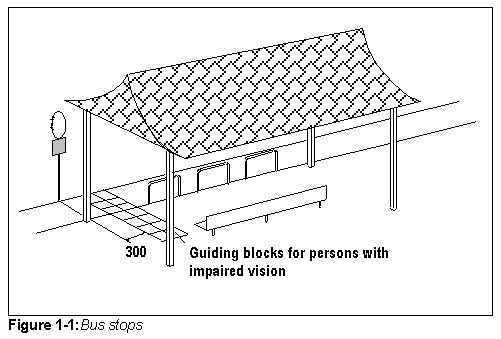
- Two rows of guiding blocks for persons with impaired vision should be provided 300 mm away from the bus stop pole on the sidewalk.
- The bus stop pole should be clearly visible after dark.
- The bus stop area should be equipped with a roof and bench(Fig.1-1)
Reference figure:
Bus interior
| Application | General | Urban application | Information technology | Rural application | Safety | |||
| External environment | Public building | Housing | Public transport | |||||
| Physical | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
| Visual | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
| Hearing | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
| Intellectual | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
Recommendation:
Doors
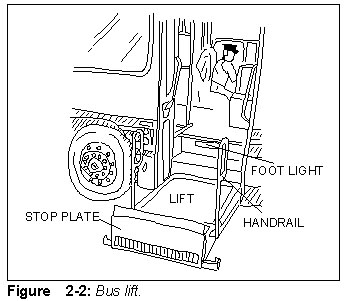
- Bus doors need to be wide enough for wheelchair users (minimum 900 mm).
- A low-level step should be installed.
- In the doorway, a handrail, footlight and floor of non-slip material should be provided.
- Apparatus such as a lift or ramp should be installed in the doorway for wheelchair users.
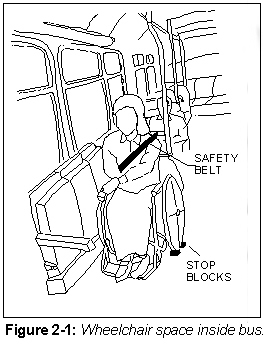
Wheelchair space
- Space for a wheelchair should be provided in an appropriate position, without preventing other passengers from getting on and off.
- The position of that space should be indicated, inside and outside the bus, using the standard symbol for wheelchair accessibility.
- Wheel stoppers and wheelchair safety belts should be provided.
Seats
- Two designated seats for persons with disabilities or elderly persons should be situated near the doors of buses.
Alighting buzzers
- An appropriate number of alighting buzzers should be provided in positions which are easily accessible for seated or standing passengers.
- The push button of an alighting buzzer should be clearly visible and of adequate size.
Information signs
- Information on the names of all stops along a bus route should be indicated inside the bus by displaying text in a suitable position. Preferably, this information should also be announced verbally.
- Information on a route and its final destination should be displayed outside the bus in large text, especially on the front and side of the bus. This information should be illuminated by an internal light to make it readable in the dark.
Reference figure:
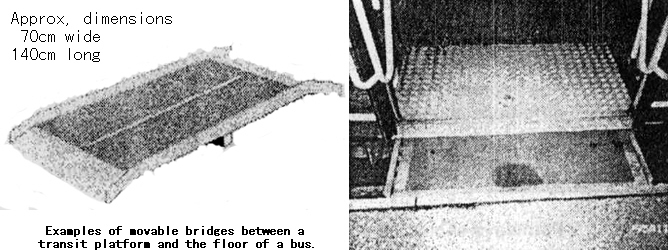
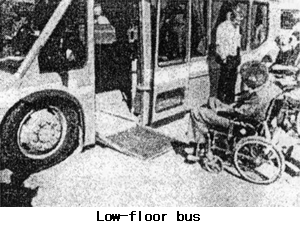

Railway stations
| Application | General | Urban application | Information technology | Rural application | Safety | |||
| External environment | Public building | Housing | Public transport | |||||
| Physical | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
| Visual | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
| Hearing | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
| Intellectual | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
Recommendation:
Approach to station
- The approach should not have a difference in level. If a level difference is unavoidable, install a ramp or a ramp plus staircase.
Paved surfaces
- Pathways should be constructed of non-slip material. At places where there is a difference in level, such as where staircases meet floors, it is desirable that the appearance of the surface material should be changed using colour contrast both immediately before and after that area.
- The approach pathway should have guiding blocks for persons with impaired vision.
- If the approach pathway is parallel to a road for vehicles, enhance the safety of pedestrians by installing guard rails.
Station entrances and exits
- The station entrance/exit should not have a difference in level. If a level difference is unavoidable, install a ramp or a ramp plus staircase.
- It is desirable that space be marked out near the entrance/exit for vehicles carrying wheelchair users.
Concourse
- The width of the concourse should be at least 1,800 mm.
- The concourse should not have a difference in level. If a level difference is unavoidable, install a ramp or a ramp plus staircase.
- The floor surface of a concourse should be made of a non-slip material. In places where there is a difference in level, such as stairs, it is desirable that the appearance of the surface material should be changed using colour contrast.
- Ensure that columns, signboards and other fixtures do not protrude from wall surfaces.
- Install guiding blocks on the concourse for persons with impaired vision.
Stairs
- A flight of stairs should be of gentle gradient.
- Handrails for stairs should be installed on both sides.
Lifts (elevators)
- Install a lift (elevators) as a means to enable passengers with disabilities to move between floors.
- For the lift (elevators), install two guiding blocks for persons with impaired vision 300 mm away from the call button.
WC
- Install a toilet and washstand suitable for use by wheelchair users and other passengers.
Reservation or information counters
- Reservation or information counters should have unobstructed approaches for wheelchair users.
- Counter heights should not be in excess of 850 mm.
Ticket gates
- At least one of the ticket gates should be wide enough to allow wheelchair users to pass through easily.
- One of the ticket gates should have a continuous line of guiding blocks for persons with impaired vision.
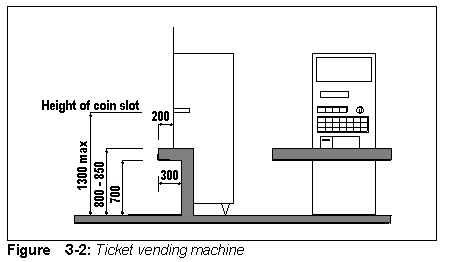
Ticket vending machines
- The coin slot should be at a suitable height for easy insertion of coins by wheelchair users (Fig.3-2)
- A knee recess beneath the ticket vending machines should be provided.
- Install guiding blocks for persons with impaired vision 300 mm away from the ticket vending machine.
- The fare buttons, cancel buttons and other information buttons should be written in Braille or in a distinct relief pattern.
Information
- The information board should be made easily readable by using sufficiently large text size. distinct contrast and illumination.
- It is desirable that, a printed version of the train schedule, the fare table and other travel information should be in Braille.
- Information on train arrivals and departures must be visually indicated by, for example, using an electronic or electric signboard, in addition to broadcast announcements.
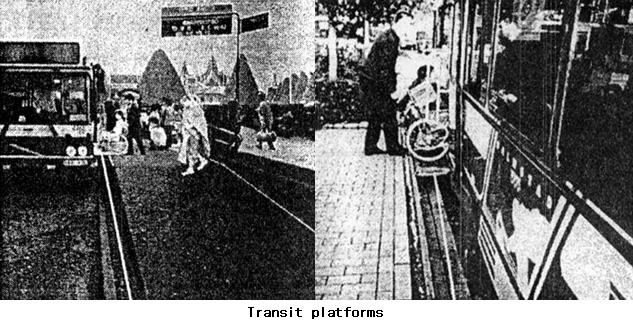
Platforms
- The platform should have one row of dotted guiding blocks for persons with impaired vision, 800 mm or more from the edge.
- A fence should be installed at both ends of the platform to protect sight-impaired passengers from falling off.
- The paved surface of the platform must be made with a non-slip material.
- Stairs, kiosks and dustbins on the platform must not hinder the clear passage of persons with impaired vision and wheelchair users.
- A bench should be installed on the platform.
Reference figure:
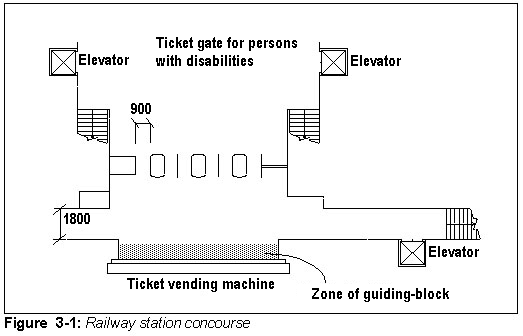
Accessible railway station




Railway cars
| Application | General | Urban application | Information technology | Rural application | Safety | |||
| External environment | Public building | Housing | Public transport | |||||
| Physical | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
| Visual | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
| Hearing | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
| Intellectual | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
Recommendation:
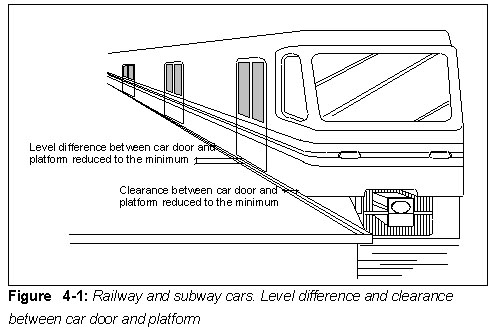
Railway and subway car doors
- Car doors should be wide enough for wheelchair users (minimum 900 mm).
- The gap between car doors and the platform should be reduced to an absolute minimum (Fig.4-1)
Aisles
- Aisles should be wide enough for the passage of wheelchairs.
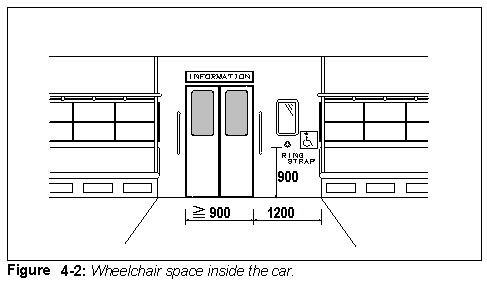
Wheelchair space
- A space for a wheelchair should be made available at the side of the door.
- The space should be indicated inside and outside the car by using the universally recognized symbol for wheelchair accessibility.
- Install a ring-strap or other appropriate safety grip for wheelchair users to hold on to.
Seats
- An appropriate number of designated seats for passengers with disabilities and for elderly people should be provided near doors.
Information signs and announcements
- Install a map of train routes.
- Announce and provide in each car a visual display of the names of stations in route.
Reference figure:



Taxi, aircraft, ship and ferry
| Application | General | Urban application | Information technology | Rural application | Safety | |||
| External environment | Public building | Housing | Public transport | |||||
| Physical | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | x |
| Visual | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
| Hearing | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
| Intellectual | . | . | . | . | x | . | x | . |
Recommendation:
Taxi stand
- Two rows of guiding blocks for person with impaired vision should be provided 300 mm away from the taxi stand pole on the sidewalk.
- The taxi stand pole should be visible after dark.
- For wheelchair users to be able to approach a taxi easily, sudden level differences from the taxi stand to the road need to be eliminated
Taxi interior
- Taxi should be adapted to allow passengers to get in and out of them while remaining seated in their wheelchairs.

Airport
- For details, see "Railway station".
Aircraft interior
- Doors need to be of a suitable width for wheelchair users.
- Aisles must be wide enough for wheelchair users.
- Accessible WC on board aircraft.
- Plugs should be accessible for passengers requiring their respirators to be plugged into electricity outlets.
Piers and jetties
- Terminal building - similar to "Railway station", except for the platform.
Ship and ferry interior
- Doors should be wide enough for wheelchair users.
- Aisles should be wide enough for wheelchair users.
- Accessible WC on board ship.
- Safety belts should be provided on board for wheelchair users to enhance their stability as required during sailing.

Go back to the Contents
ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMISSION FOR ASIA AND THE PACIFIC
Major issues in transport and communications: Promotion of user-friendly public transport systems for people with disabilities
- Appendix -
E/ESCAP/CTC(3)/5
16 October 1997
