20 October 1997 (Mon)
Welfare Services for Persons with Disabilities in Japan
by
Mr. Hideharu Uemura, Specialist for International Cooperation
International Cooperation Office
National Rehabilitation Center for the Disabled (NRCD)
I. Introduction
Most of the systems of social welfare in Japan today have their basis in laws enacted after World War II. Japanese government issued A Prospectus on Emergency Relief Measures for Needy People in 1945. On the other hand, GHQ addressed the four basic principles related to national assistance in the formal memorandum to the Japanese government in 1946, as follows:
- 1) National relief should be carried out on an equal basis without discrimination.
- 2) The protection of those who are poor and in need of daily necessities should be assisted under the responsibility of the state.
- 3) The responsibility should not be placed on others but on the state.
- 4) The amount of the budget for assistance should be sufficient for the protection of the poor and should not be limited.
Japan Constitution was established in 1946 and clearly assumed a major responsibility for social welfare. The first clauses of the Article 25 of the Constitution states as follows: "All people shall have the right to maintain the minimum standards of wholesome and cultured living," and the second clause states that "the State must make efforts to promote and expand social welfare, social security and public health services to cover every aspect of the life of the people."
- 1946 Daily Life Security Law
- 1947 Child Welfare Law
- 1949 Law for the Welfare of Physically Disabled Persons
- 1950 Mental Hygiene Law (Law Concerning Mental Health and Welfare for Mentally Disabled, Amended 1993)
- 1951 Social Welfare Service Law
- 1960 Law for the Welfare of Mentally Retarded Persons
- 1961 National Health Insurance Law
National Pension Law - 1963 Law for the Welfare of the Aged
- 1964 Law for Maternal and Child Welfare
II. Outline of welfare services for persons with disabilities
1. Welfare services for physically disabled persons
The establishment of the Law for the Welfare of Physically Disabled Persons in 1949 took welfare for persons with disabilities beyond the existing framework of poor relief measures and rehabilitation services for disabled veterans and set in place rehabilitation services that have continued to benefit all physically disabled persons.
The primary issue of rehabilitation services for physically disabled persons is to create conditions under which they can live at home or in their communities.
To this end, the Government must push ahead with comprehensive measures that deal not only with social rehabilitation, but also with public education, health and medical care, education, employment, income security and the living environment.
1) Definition of physically disabled persons
The definition of physically disabled persons in Japan is provided in the Law for the Welfare of Physically Disabled Persons and there are various evaluation standards establishing the severity of the impairment in the form of ratings from Grades 1 through 6.
(1) Permanent visual impairment as listed in the following.
- Visual acuity(as measured in accordance with the International Vision Chart and measured degree of correctness; hereafter the same) of both eyes being 0.1 or less.
- Visual acuity of one eye at 0.02 or less and the other at 0.6 or less.
- Visual field diameter 10 degree or less of both eyes.
- Visual field defect more than 50% of both eyes.
(2) Permanent hearing impairment or impairment of balance function as listed in the following.
- More than 70dBHL in each ear.
- One ear more than 90dBHL, the other more than 50dBHL.
- Less than 50% of hearing intelligibility.
- Severe impairment of balance.
(3) Impairment of voice, speech or mastication function.
- Total loss of voice, speech or mastication function.
- Severe and permanent impairment of voice, speech or mastication function.
(4) Impairment of the limbs trunk as listed in the following.
- Severe and permanent impairment of one upper limb, one lower limb or trunk.
- Loss of the thumb of one upper limb upward of the knuckle joint or loss of two or more fingers of one upper limb including the forefinger upward of the knuckle joint.
- Loss of one lower limb upward of the lisfrance joint.
- Loss of all toes from both lower limbs.
- Severe impairment of the thumb of one upper limb or severe and permanent impairment of three or more fingers of one upper limb.
- In addition to the factors as listed in the foregoing, other impairments that are acknowledged to be of degrees higher than the impairments as listed in 1 through 5 of the foregoing.
(5) Impairments of the functions of the heart, kidney, respiratory organs, bladder, rectum and small intestine that are permanent and acknowledged as being of a degree to cause extreme limitations in daily living.
2) Welfare measures for physically disabled persons
(1) Issue the Certificate of Disability(Service ID)
(2) Measures for reducing or correcting impairment, medical examination and rehabilitation counseling.
- Provision of medical rehabilitation
- Medical examination at home
(3) Provision of prosthetic appliances, technical aids and daily use appliances.
- Provision of prosthetic appliances
Types of prosthetic appliances
- Visual Impairment ............ white-cane, artificial eye, shaded glasses, spectacles and Braille writer
- Hearing Impairment ........... hearing aid
- Speech Impairment ............ artificial larynges
- Limb/trunk Impairment ........ artificial limbs, wheelchair, walking-sticks, electronic wheelchair, seating systems etc.
- Bladder or rectum disorders .... devices for stoma
- Provision of technical aids and daily use appliances
Types of technical aids and daily use appliances
- Visual Impairment ............ tape recorders for the blind, thermometers, watches(sound-type/tactile-type), time switches, calculators(sound-type), Braille typewriters, electro-magnetic cooking utensils etc.
- Hearing Impairment .......... Fax machine, indoor light signal system
- Speech Impairment ............ speech aids
- Limb/trunk Impairment ........ bathtubs, toilet bowls, special mattresses, bathing stretchers, special beds, special urinals, posture-changing devices, word processors, electric toothbrushes etc.
(4) Welfare measures for physically disabled persons at home
- Provision of the special allowance for persons with disabilities (in 1995)
- special allowance for persons with disabilities ........ \26,230 per month
(disability basic pension<first degree> ................ \81,825 per month
<second degree> .............. \65,458 per month)
- special allowance for persons with disabilities ........ \26,230 per month
- Dispatch of home helpers
- Short stay program for persons with disabilities
- Day services for persons with disabilities
- Respite care for persons with disabilities living at home
(5) Measures to promote participation of persons with disabilities
- Publication of Braille information and talking books for the blind
- Guide dog for the blind
- Training and dispatch sign language interpreter
- Driving lesson for persons with disabilities
- Sport classes for persons with disabilities
2. Welfare services for mentally retarded persons
(1) Issue the Certificate of Disability(Service ID)
(2) Early detection of mental retardation
- Examination for congenital metabolic anomalies
- Health Examination(Infant, 1.5 years old, 3 years old, etc.)
(3) Early treatment of mental retardation
- Counseling and guidance at health center, child guidance center, etc.
- Day care services in day-care center
(4) Welfare services for mentally retarded persons
- Rehabilitation program for mentally retarded persons
- Dispatch of home helpers
- Short stay program for mentally retarded persons
- Day services for mentally retarded persons
- Respite care for mentally retarded persons
- Dental clinic for mentally retarded persons
3. Welfare services for mentally disabled persons
(1) Issue the Certificate of Disability(Service ID)
(2) Social rehabilitation services
- Counseling and guidance at health center, social rehabilitation facilities.
- Social adjustment training program
- Support of daily life at group home
- Work training at sheltered workshop
- Providing workplace at welfare workshop
- Providing long-term residency at welfare home
- Recovery training at supported dormitories
(3) Community mental health services
- Visiting guidance and support for user group
- Mental health and welfare counseling
(4) Medical services
- Outpatient medical care
- Medical care and protection for hospitalized persons
III. Population data of persons with disabilities
1. Number of physically disabled persons who live at home
1) 18 years old and over
- Limb/trunk impairment 1,553,000(57.1%)
- Internal disorders 458,000(16.8%)
- Hearing/speech impairment 358,000(13.2%)
- Visual impairment 353,000(13.0%)
Total 2,722,000(100%)
2) 0 - 17 years old
- Limb/trunk impairment 48,500(59.9%)
- Internal disorders 17,500(21.6%)
- Hearing/speech impairment 11,200(13.8%)
- Visual impairment 3,900( 4.8%)
Total 81,000(100%)
2. Number of mentally retarded persons
|
Total |
Living at home |
Institutionalized |
|
|
Total |
385,100 |
283,800 |
101,300 |
|
Under 18 years old |
115,100 |
100,000 |
15,100 |
|
18 and over |
254,400 |
168,200 |
86,200 |
|
Unknown |
15,700 |
15,700 |
3. Number of mentally disabled persons
Estimated numbers of mentally disabled persons in 1994 is about 1,570,000
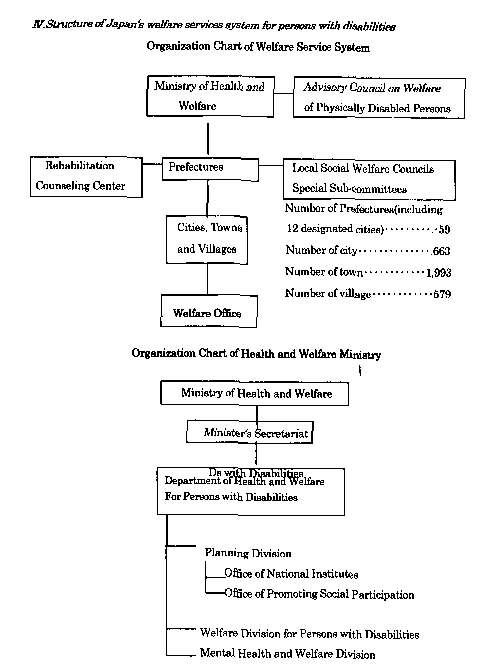
From "Resource Book of Training Course for Leaders of Persons with Disabilities 1997"
Japanese Society for Rehabilitation of Disabled Persons
