Disabled Village Children
A guide for community health workers,
rehabilitation workers, and families
PART 1
WORKING WITH THE CHILD AND FAMILY:
Information on different Disabilities
B. Recognizing, Helping with, and Preventing Common Disabilities
CHAPTER 16
Juvenile Arthritis
Chronic Arthritis in Children
HOW TO RECOGNIZE IT
- The arthritis (joint pain) often begins between the ages of 5 and 10, but may begin in very young children or teenagers.
- Usually it keeps getting worse for several years.
- There are times when the pain and other signs get better, and times when they get worse.
- It affects different children in different ways. It can be mild or very disabling.
Signs
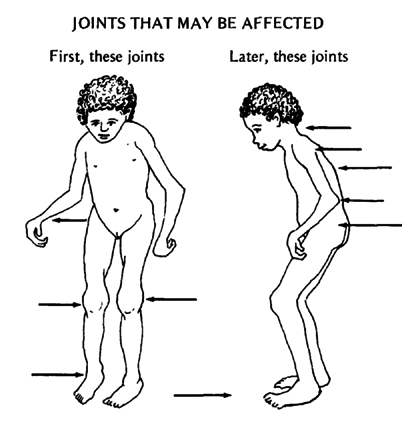
- Joint pain. Often begins in the knees, ankles, and wrists. Later it affects the neck, fingers, toes, elbows, and shoulders. Still later, the hips and back may be affected.
-
Joints are especially painful and stiff in the morning (morning stiffness).
-
Fevers and rash that come and go. (in some children these are the first signs.)
-
The knees become large and may turn inward.
-
Pain may make it difficult to straighten the knees, hips, and other joints. The cords may tighten, forming contractures, and the bones may gradually become dislocated.
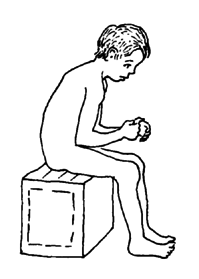
A child with severe arthritis often sits with his arms and legs bent in the least painful position. Without exercise and good positioning, contractures may form so that he cannot walk or even stand up.

- Children with severe arthritis in the neck and jaw may have a small, short chin.
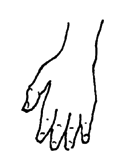
- The fingers may become very thin and deformed, or thick, with slender tips.
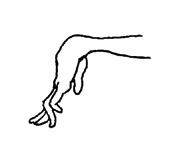
- Wrists and ankles may become stiff and bent.
- Contractures may develop in the fingers or toes, and with time the bones may fuse (stick together).
More information about JUVENILE ARTHRITIS
|
There are 3 types of juvenile arthritis: 1. Fever type: There are times during the day when the child has a high fever, a rash, and feels ill and tired. He looks very sick. The joint pain seems less important, and it begins days or months after the other signs. There may be severe anemia (child looks pale). 2. Many-joints type: More than 5 joints with pain. The child hurts a lot, and moves very little. Often severe contractures develop. The child does not grow much, and his sexual development is delayed. 
3. Few-joints type: Fewer than 5 joints affected. it can affect more joints after months or years. If the back is affected, it is rnore likely that severe arthritis will continue when he is adult. It may affect the eyes, causing iritis and blindness. |
What causes it?
The exact cause of juvenile arthritis is not known, but it has something to do with the body's 'immune system' (defenses against disease). This begins to attack not only germs, but parts of the body itself. The problem is usually not hereditary, and is not related to climate, diet, or the child's way of life. It is not caused by anything the parents may have done. It cannot spread from one child to another. It does not affect the child's intelligence.
Will the child get worse, or better? What about her future?
The progress of the disease varies a lot. Typically, there are times when the joints become very painful, and times when they hurt less. Often the joint pain and disability will get worse and worse for several years, then gradually start to improve. Two out of 3 children will stop having active arthritis after 10 years, although the damage already done to the joints may cause some permanent disability. Some children will continue to have arthritis when they are adults, but it is usually milder.
|
Most children with arthritis will become adults who walk, work, and have full and happy lives. |
How does it affect the child and her family?
A child with severe arthritis suffers a lot. After a night of being kept awake by the pain, the child may be irritable, sad, and dull. But when the pain is less, she may be friendly and lively.
Since the arthritis often continues to get worse for years, even with all efforts to cure it, both the child and her family may lose hope and stop trying.
Also, the family may not understand how much the child is suffering, because the cause of the pain does not show. (in children's arthritis the joints do not usually get red, as they do in adults.) So the family sometimes calls the child a 'cry-baby' or a trouble-maker. The child may feel abandoned or guilty. The situation is very hard on the whole family.
The family needs the help and support of understanding neighbors, health workers, and, if possible, a rehabilitation worker. They need to understand that by continuing exercises, therapy, and medicines-often for years-the child does have hopes of getting better. If therapy takes the form of games with other children and family members, it may help both her body and spirit.
SECONDARY PROBLEMS
When parts of the body do not get enough movement or exercises, joint contractures are common. With time, the bones may become fused (joined together) or dislocated. Also, the muscles that straighten the arms and legs become very weak. However, with exercises and with enough movement and good positioning, all these problems can be prevented or made less severe.
Managing juvenile arthritis
The child will need:
- medicine to relieve the pain and help prevent damage to the joints
- plenty of rest, keeping the body in good positions
- exercises and movement to prevent contractures and deformities, and to keep the muscles strong
- mental, physical, and social activities, so that the child's life is full and satisfying
- if necessary, aids, and braces or casts to correct contractures and to help the child to move about
MEDICINES
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is usually the safest and best medicine. It not only helps the pain, but also reduces inflammation and damage in the joints. For precautions and doses, see the INFORMATION SHEET on Page 134.
Medicines that generally should NOT be used:

Corticosteroids have a strong anti-inflammatory effect, but they are dangerous. Although they quickly reduce the pain, joint destruction continues. Steroids make the child's body less able to fight infection, stop his growth, and weaken his bones so that they break easily. If the child takes a lot of steroids, his face becomes round and a hump of fat forms on the back of his neck and shoulders. As a rule,steroids should be used only when the child's life or eyesight is in danger. Steroid eye-drops at the first signs of iritis can prevent blindness.
Gold salts. Gold combined with sodium and sulfur, in injectable form, sometimes helps when aspirin is not effective. But it is very toxic (poisonous) and its use should be limited.
Indomethacin (Indocin), phenyllbutazone, and related medicines are so toxic that they should not be given to children.

WARNING: We mention corticosteroids, indomethacin, and phenylbutazone because many doctors prescribe them unnecessarily, putting the health or life of the child in danger. If a doctor prescribes one of these medicines for a child, get advice from other doctors before using it. |
REST AND POSITION
Children with arthritis need a lot of rest. They tire easily, and should have a chance to rest often. Help the child to be in positions that keep the arms, wrists, hips, and legs as straight as possible.
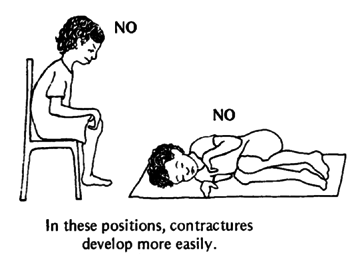
Although it may hurt more, it is better for the child to lie on her back or stomach, not on her side with her legs bent. When pain is worst, alternate rest with legs straight and slightly bent. |
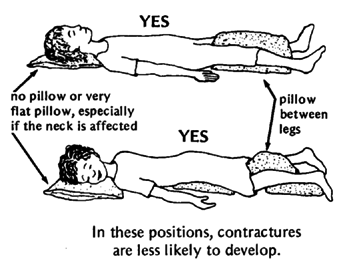
Rest and sleep with the arms and legs as straight as possible. Use pillows only in a way that gently helps the joints straighten more. Let the legs slowly straighten under their own weight. |
EXERCISES AND MOVEMENT
Our goal is to prevent contractures and dislocations, and to maintain the fullest possible range of motion for the body. So exercises are needed to strengthen the muscles that straighten the joints.
HOW PAIN CAUSES CONTRACTURES
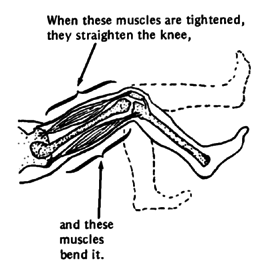
|
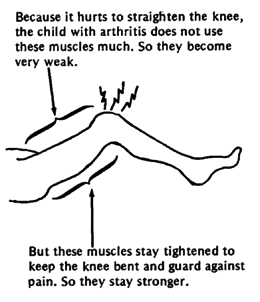
|
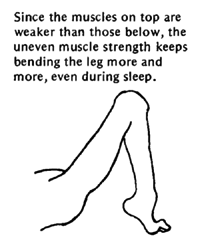
NOTE: This kind of uneven muscle strength is called muscle imbalance. |
Because contractures from arthritis result mainly from unequal muscle strength, it is important that the child do all exercises and activities in ways that will strengthen the weak muscles that straighten the joints, not the muscles that bend them. For example:
|
Do exercises that work this muscle. 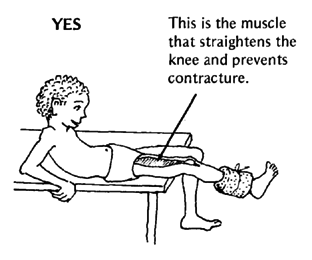
STRENGTHEN MUSCLES THAT STRAIGHTEN THE JOINT. |
|
But do not do exercises that work this muscle. 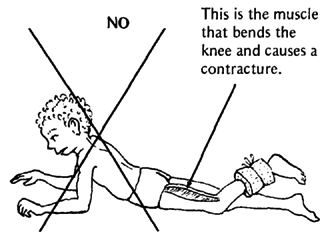
DO NOT STRENGTHEN MUSCLES THAT BEND THE JOINT. |
Follow this same logic with all exercises and activities. And look for ways to make the exercises useful and fun.
For example, Alicia has arthritis and can no longer walk by herself or straighten her arms and legs completely. As a way of moving herself about and getting some exercise, she can sit on a chair with casters, as shown here. But she should be careful to move in a way that helps prevent contractures.
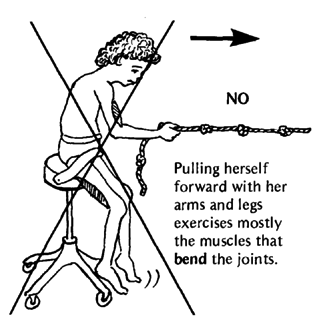
This can make contractures worse. |
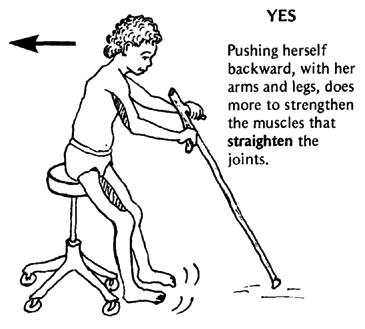
This helps prevent contractures. |
Helping the child to strengthen the right muscles
One problem with exercises is that, when either you or the child try to straighten a joint, pain-or the fear of pain-can cause her to tighten the muscles that bend it. For example:
|
If you pull like this, the muscles that bend the elbow will pull against you -and get stronger. 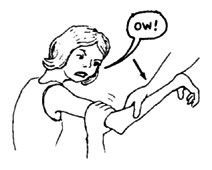
The muscles that straighten the elbow will not be used -and will get weaker. |
Even if the child herself tries to straighten her elbow, the pain will cause the stronger, bending muscles to tighten. 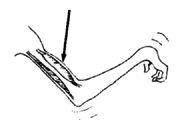
As a result, these exercises may strengthen the bending muscles instead of the weaker straightening muscles. This means that these exercises can actually make contractures get worse! |
EXERCISES WITHOUT MOTION
So it is important that the child learn to do exercises that strengthen the muscles that pull against contractures, not those that make them worse. This will be easiest and least painful if she does exercises without motion.

First help her to learn which muscles move parts of her body in different directions.
Have her exercise these muscles by relaxing and tightening them, without moving her arm.

Then help her find interesting ways to strengthen the muscles that need it without moving them. For example, she can lean on a fence like this.
Everyday she can step a little farther back from the fence, to take more weight on her arms.
Notice that this exercise also strengthens her knee-straightening muscles and helps stretch her heel cords, wrists, hips, back, and neck, in order to look the llama in the eye.
|
Note: We have shown these exercises in a girl who already has contractures. But it is best to start them before contractures begin. |
You can figure out similar exercises without motion for all the weak muscles that need strengthening to help prevent or correct contractures.
For example, to strengthen the knee-straightening muscles, the child can lie on her back with her leg as straight as possible. Have her tighten the muscles on top of her thigh (without tightening those underneath) and count to 25. Then relax and repeat 10 times. She should do this 3 or 4 times a day. Again, look for ways to make it more fun.
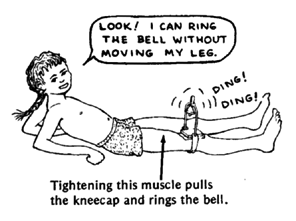

Progression of exercises for the child with an ARTHRITIC KNEE
(Arthritis often starts in the knee and later affects other joints.)
CONCEPTS:
- Strengthen the muscles that straighten the knee (without strengthening those that bend it).
- Do not move the knee when doing exercises.
- Keep changing the position in which you do the exercise, and add weights to make the exercises harder as the child's strength increases.
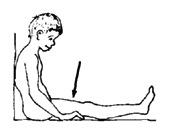
First exercise: leg on ground
First do the exercise without motion lying down.
Tighten here without moving and count to 25. Relax and repeat 10 times. Do it 3 or 4 times a day.
After a few days, do it sitting up.
Tighten here without moving.
Second exercise: straight leg raise
1. With the leg straight, tighten the muscles on top of the thigh (as in the first exercise).
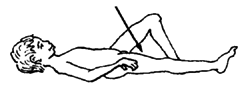
2. Then lift the leg without bending the knee, and slowly count to 5 or 10.
3. Lower the leg slowly.
4. Rest.
When you lift the leg, be sure that the knee points up or slightly out to the side.
Do not let knee bend at all. (If the knee bends even a little when you lift the leg, it means that the muscles here are still too weak. Go back to first exercise.)
When the child can do this exercise lying down without bending his knee, begin putting weights on his leg:
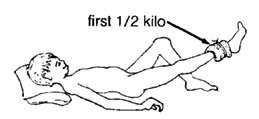
|
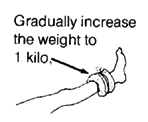
|
For the weight, you can use a small bag full of sand. |
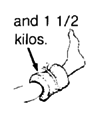
|
After a few days, have him do the same exercise sitting up:*
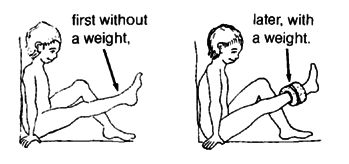
Again, gradually increase the weight. Begin with half a kilo, and build up to 5 kilos. But do not increase the weight until the child can do the exercise at the first weight without bending his knee.
|
*CAUTION: Do not do sitting exercise if the child has arthritis in the hip, or hip contractures. It uses the hip-bending muscles that will make the contractures worse. |
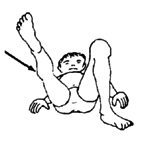
When the child can do the exercise at 2 kilos without bending her knee, she can begin doing the following variation. Keep the leg raised the whole time.
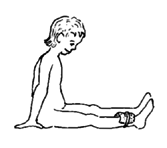
1. Tighten the muscle on top of the thigh. |

2. Lift the leg, keeping it straight. |
|

3. Move the leg to the side and turn it outward. |

4. Move the leg back in and turn it inward. |

5. Lower the leg and relax. |
|
IMPORTANT: If there is also arthritis in the hip, or hip contractures, do these exercises lying down, not sitting up. |
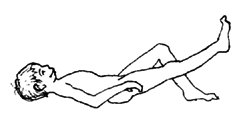
Third exercise: knee slightly bent
|
1. Lie down with a rolled towel or blanket under the knee. 
|
2. Turn the leg out to the side. 
|
|
3. Lift the foot and slowly count to 5 or 10. 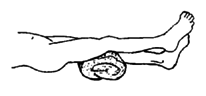
|
4. Lower it slowly. 5. Rest. 6. Repeat the exercise 10 to 30 times. |
Make sure that only the foot is raised, not the thigh, and that the knee is lifted as straight as possible.
As the child gains strength, continue with the same series of steps as for the second exercise.
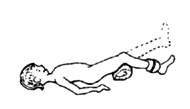
1. Lying down, lift the foot with a weight on it. Build weight up slowly to 5 kilos. |
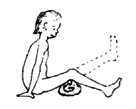
2. Sitting up, lift the foot without a weight. |
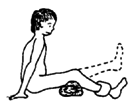 3. Sitting up, lift the foot with a weight. (Build up to 5 kilos.) |
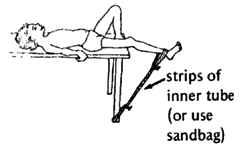
If arthritis or contractures have begun in her hip, it is best to do the exercise lying down with the hip as straight as possible (nothing under the knee). |
|
Do these 2 (Step 2, 3) exercises only if there is no danger of hip contractures. |
To strengthen the muscles, continue the exercise until the child can no longer hold the leg straight or it begins to shake slightly. The more often the child does these exercises the faster the muscles will get stronger. These exercises can be done even when the joint is swollen and painful. However, if the joint hurls more during or after the exercise, use less weight and repeat fewer times.
Exercising an ARTHRITIC KNEE through daily activities
WALKING. Walking is one of the best exercises for strengthening the thigh-if the child puts some weight on the leg.
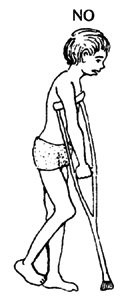
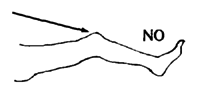
For arthritis, try to use canes, not crutches. A crutch can cause contractures. WARNING: If a child uses a crutch and does not step down with his leg, this strengthens only the muscles that bend the leg. |
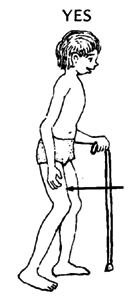
A cane helps strengthen weak muscles and prevent contractures. If he uses a cane, he must put some weight on the leg. This strengthens the muscles that straighten the leg. |
During the times when the child's arthritis is less painful, she should be active. It is fine for her to run, ride a bicycle, or take long walks-as long as this does not cause much joint pain.
These activities strengthen weak thighs.
|

Walking uphill exercises the thighs more than walking on flat ground. |

After the child can walk fairly well without aids, a good exercise is walking on the heels. (if the arthritis also affects the ankles, this may not be possible. But try.)
SWIMMING. Swimming is one of the best exercises for a person with arthritis.
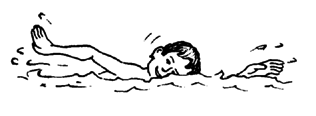
Floating and play in water also is good exercise. The water holds up the body and allows movement of the arms and legs without weight, yet against the gentle resistance of the water.

Range-of-motion exercises for children with arthritis
For a child with arthritis, it is important that every day he move his body, arms, and legs through as full a range of motion as possible.
|
Note: Range-of-motion exercises for different joints are described in Chapter 42. Here we discuss ways to make them easier for children with arthritis. |
But this is not always easy. Pain and stiffness make straightening of joints difficult. So before starting to exercise, take steps to calm the pain and relax the tense muscles. Aspirin helps do this. Take it half an hour before beginning exercise (or before getting up to help morning stiffness).
Heat helps relax muscles and calm pain. Suggestions for applying hot soaks and hot wax are on Page 132. If many joints are painful, it helps to lie in warm water (a little warmer than body temperature).
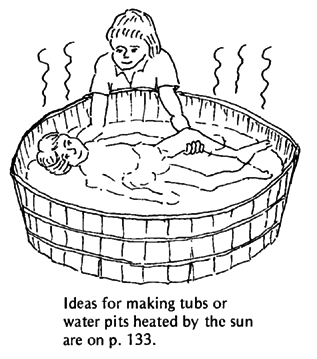
If possible, get or make a tub large enough for the child to lie straight and to stretch his arms and legs in all directions.
Warm water not only helps calm pain, but gently lifts and takes the weight off body parts. This makes motion easier. Support the child only as much as needed so that his arms and legs are loose and held up by the water. Ask him to relax completely. Let him begin to move his arms and legs. The more he relaxes, the more they will straighten as he moves.
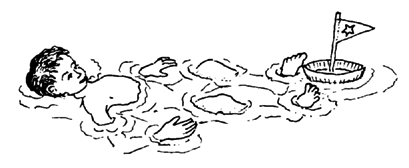
Find ways for the child to play in the water. This will help him forget his pain and make straightening the joints easier.

In moments when she has her leg or arm most straight, ask her to hold that position a moment without bending.
This way, little by little, she will find she can straighten her joints more and more.
'Floating-in-air' devices for relaxing and moving painful joints
The best way for relaxing and reducing weight to exercise arthritic joints is to float in warm water. When this is not possible, after applying hot soaks (see Page 132), the leg or arm can be hung in a simple device-loosely, as if floating in water.
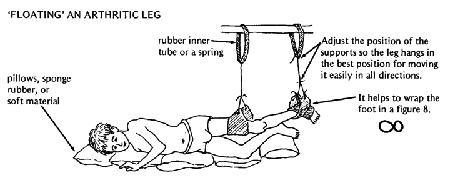
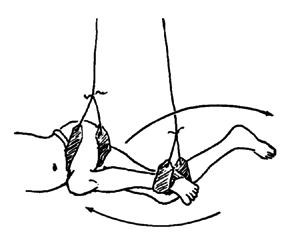
After hanging the limb, wait until the child relaxes, then have him swing it gently this way and that.
Let the leg move with its own weight as in a swing. Increase the swinging until the knee and hip bend and straighten completely (or as much as possible).
Look for ways to turn the exercise into a game.
For example, the child might knock gourds or blocks down while another child tries quickly to set them up again, and see who wins.
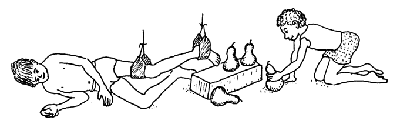
The gourds can be put farther and farther away so that he has to stretch more each time to knock them down. When his leg is most stretched, ask him to hold it that way a moment before letting it bend.
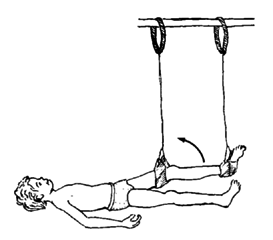
Also have the child do exercises lying on his back and swinging his leg outward (to one side). This helps prevent knock- knee contractures.
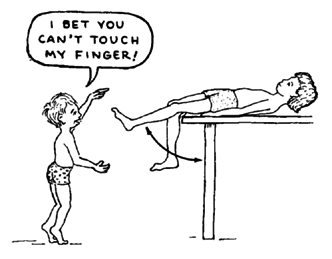
The child can also swing her leg while sitting or lying on a table edge. Encourage her to swing the leg as far up and back as possible. Turn it into a game.
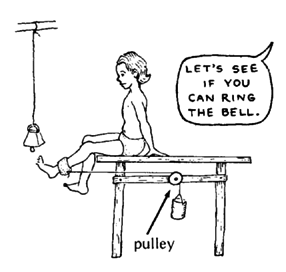
A device like this helps strengthen the muscles that straighten the knee. This way works better than a weight tied to the ankle because the pull continues even when the knee is bent.
Put stones or pieces of metal in an old can. Use only as much weight as will let the child straighten her knee completely. As the leg becomes stronger, add more weight.
Movement of the arms. This is done much like the legs:
|
LYING FACE UP 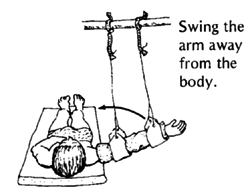
|
|
LYING ON THE SIDE 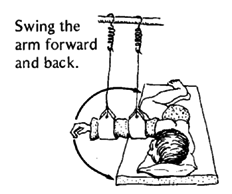
|
|
AND SITTING 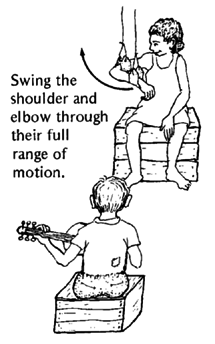
|
These movements can be done keeping the hot soaks on the arm.
Encourage the child to move her limb in a rhythmic manner - perhaps to music. Try to help her forget the pain. If she becomes interested in something else-a game or the music-this will help reduce the tightness of her muscles.
Look for ways to do these movements as part of daily activities.
CORRECTING CONTRACTURES CAUSED BY ARTHRITIS
For general information on the cause, prevention, and correction of contractures, see Chapter 8. Range-of-motion and strengthening exercises will help prevent or correct early contractures (see Chapter 42). For severe contractures, stretching aids or casts may be needed (see Chapter 59). However, when using casts or other aids to straighten contractures, it is very important to continue exercises without motion to strengthen the muscles that straighten the limb.
PRECAUTIONS FOR CASTING AN ARTHRITIC LIMB
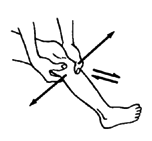
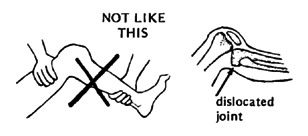
1. First examine the joint for signs of dislocation. Try moving the bones forward and backward and from side to side.
CAUTION:If the joint is partly dislocated or very loose, it is best not to use casts or stretching devices, as these can increase the dislocation. It is better to continue with the exercises, taking care not to force the joint.
2. If there are no signs of dislocation, little by little straighten the joint as far as is possible without causing much pain.
CAUTION: Do not pull like this, or you may dislocate the joint.
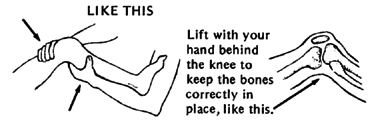
3. With the joint as straight as you can get it without too much pain, carefully cast the leg (see Page 560).
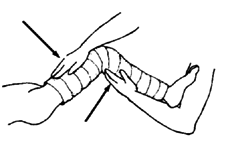
Until the cast dries, apply steady pressure here so that the bones keep their right locations and the joint stays straightened.
4. As long as the cast is in place, do without-motion exercises several times a day. This helps keep the straightening muscles strong.

5. Every 2 days remove the cast, apply heat and do range-of-motion exercises, bending and straightening the leg little by little. Then gently stretch the leg a little more, and put on another cast.
(IMPORTANT: It is best to replace the cast completely rather than to use wedges with the same cast, because of the risk of dislocation.)

6. Continue straightening the leg with new casts every 2 days until it is completely straight or does not straighten more.
Keep a record of the progress like this (see Chapter 5). This way you can tell when the leg is no longer getting straighter and it is time to stop using casts.
Homemade aids for stretching joints
Because daily movement of joints is so important with arthritis, casts should be avoided whenever possible. So try to figure out other ways to correct contractures. Use whatever materials you can find, such as plastic, bamboo, and inner tubes.
These are a few of the examples of aids invented in a Mexican village for a girl with arthritis.
|
CAUTION: Make sure that the aids pull in a way that does not cause dislocations. |
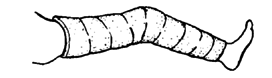
KNEE
|
METHOD 1: 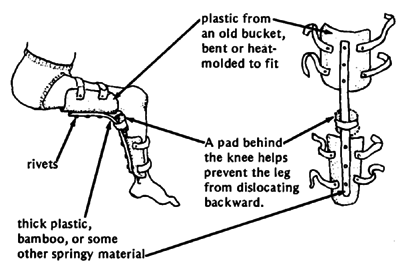
|
|
Note: The behind-the-knee aid usually works the best. It is steadier and so causes less muscle tightening. Because it holds the leg more firmly, it is less likely to cause dislocations. It is also more comfortable and less awkward.
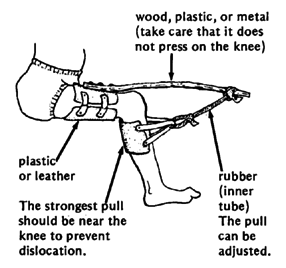
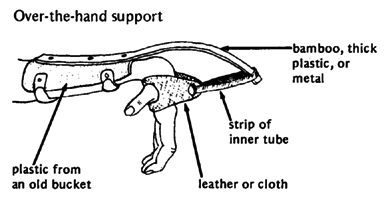
WRIST
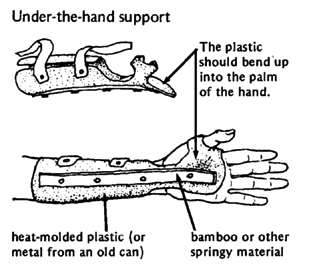
|
PRECAUTIONS in the use of aids for stretching contractures:
|
For other aids and devices for straightening contractures, see Chapter 59.
Correcting contractures of arthritic hips
Look for ways that the child can relax with her head as straight as possible. If she also has contractures in her knees, she can lie like this.
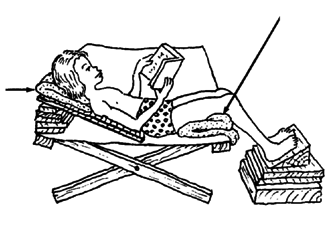
The child will relax and straighten her body more easily if she can, play or read.
Place supports or cushions behind her back and head, but just enough so that she has to straighten herself some. As her hips and neck gradually straighten, keep lowering her back and head little by little.
Give just enough support under her knees and feet to keep her hips and knees stretched. As they gradually relax, lower her knees and raise her feet little by little, so that her hips and knees straighten.
In the morning, she may be stiff and bent, and will need help to straighten like this every clay- or several times a day.
If possible, also have her lie on her belly.
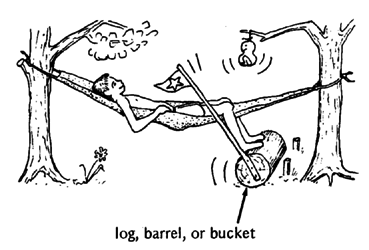
Think of games or exercises in which the child will stretch his hips and knees. In this example, the boy rolls the log to lift the flag and hit the gourd. This helps strengthen the straightening muscles of his legs.
As the child's back, hips, and knees straighten more and he gains strength, the hammock can be stretched more tightly and a heavier weight put on the top of the stick, where the flag is.
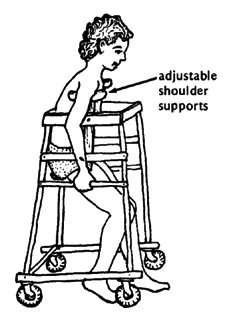
A homemade walker similar to this can help a child with hip contractures begin to walk. It also provides exercise for the straightening muscles of both the arms and legs.
As the child's hips and knees straighten more and more, the crutches and seat can be raised.
It is best if she walks backward ("Pretend you're a crab!"). This way she will strengthen the straightening muscles in her legs. Walking forward would strengthen more the muscles that bend the legs, and this could increase contractures.
LEARNING TO MOVE AND TO SMILE - the story of Teresa
Teresa has had juvenile arthritis since age 7. When her mother first brought her to PROJIMO from a distant village at age 14, her body had stiffened into the shape of a chair. Her eyes were the only parts of her body she could move. Her joints hurt her so much that she spent every night crying. Years before, a doctor had prescribed aspirin for her pain. But the aspirin began to give her severe stomach pain, so she stopped taking it.
Once Teresa was a cheerful, active little girl. She had completed 3 years of school. Now she was sad and felt hopeless. She would cry out with pain each morning when her father carefully lifted her out of bed and sat her in a chair. She rarely spoke and never smiled.
When Teresa arrived at PROJIMO she had severe contractures of her wrists, fingers, elbows, hips, knees, ankles, and feet. The rehabilitation team had her start using aspirin again, but with care that she take it with meals, lots of water, and an antacid. They then began a long, slow process of therapy, part of which we show in the following photos.

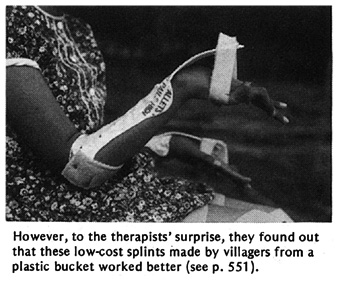 See Page 551.
See Page 551.
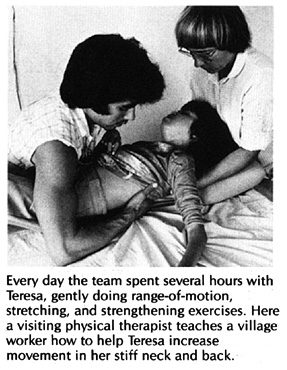
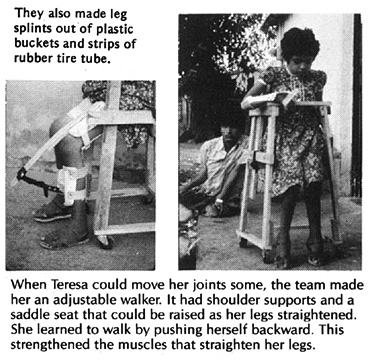
Teresa was improving steadily. She began to talk, smile, and to take interest in things. An older brother came to visit for a few weeks. He learned about her exercises and therapy so he could help her when they returned to their village.
Unfortunately, soon after Teresa went home she became ill with dengue (break bone fever) and nearly died. Her family stopped both exercises and medicines. When she returned to PROJIMO 6 weeks later, she was as stiff and bent as when she first came. She was so depressed she spoke to no one. The team began her rehabilitation all over again.
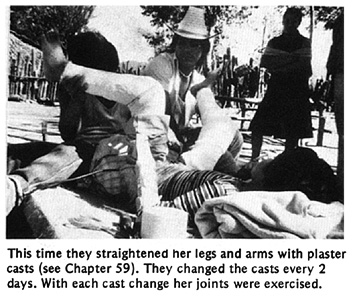

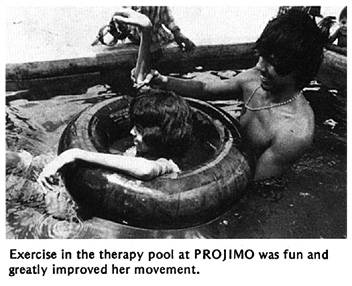




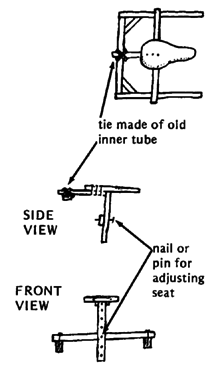
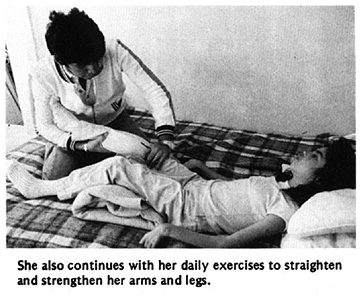
As Teresa's legs and arms straightened, her neck bent forward more and more. She could not lift her chin from her chest. The village workers made her a head support, attached to a firm cloth around her chest. Over a period of months, the support gently brought up her head.

|
|

|
|

|

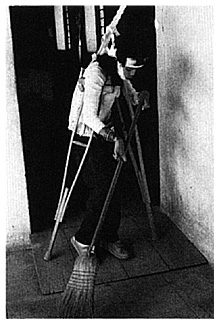
At home, Teresa now helps care for her younger brothers and sisters. She and her family share the household tasks. Before, others had to take care of her.
Disabled Village Children
A guide for community health workers,
rehabilitation workers, and families
by David Werner
Published by
The Hesperian Foundation
P.O. Box 11577
Berkeley, CA 94712-2577
